ISX-9E
Pharmacology 
ISX-9 is an experimental and toxic neurogenesis enhancer that increases neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation [1][2]. It has been shown in studies to enhance memory and lower addictive qualities of opioids [6]. ISX-9 not not have any clinical human trials.
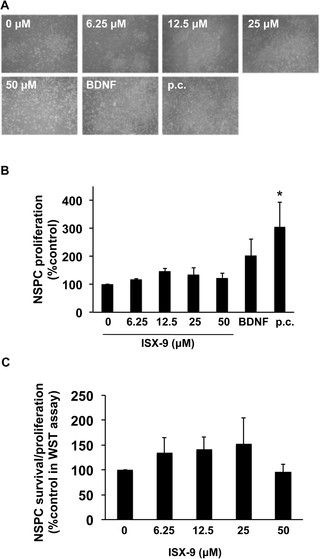
ISX-9 enhances cognitive capacity in some ways, but comes at the cost of Oligodendrocyte cell death [2]. If you don't know the importance of Oligodendrocytes, Oligodendrocytes generate myelin to facilitate efficient neuronal transmission and provide metabolic and trophic support to neurons. Myelin is very important in protecting neurons, and deficits are seen in Huntington's Disease and Multiple sclerosis.
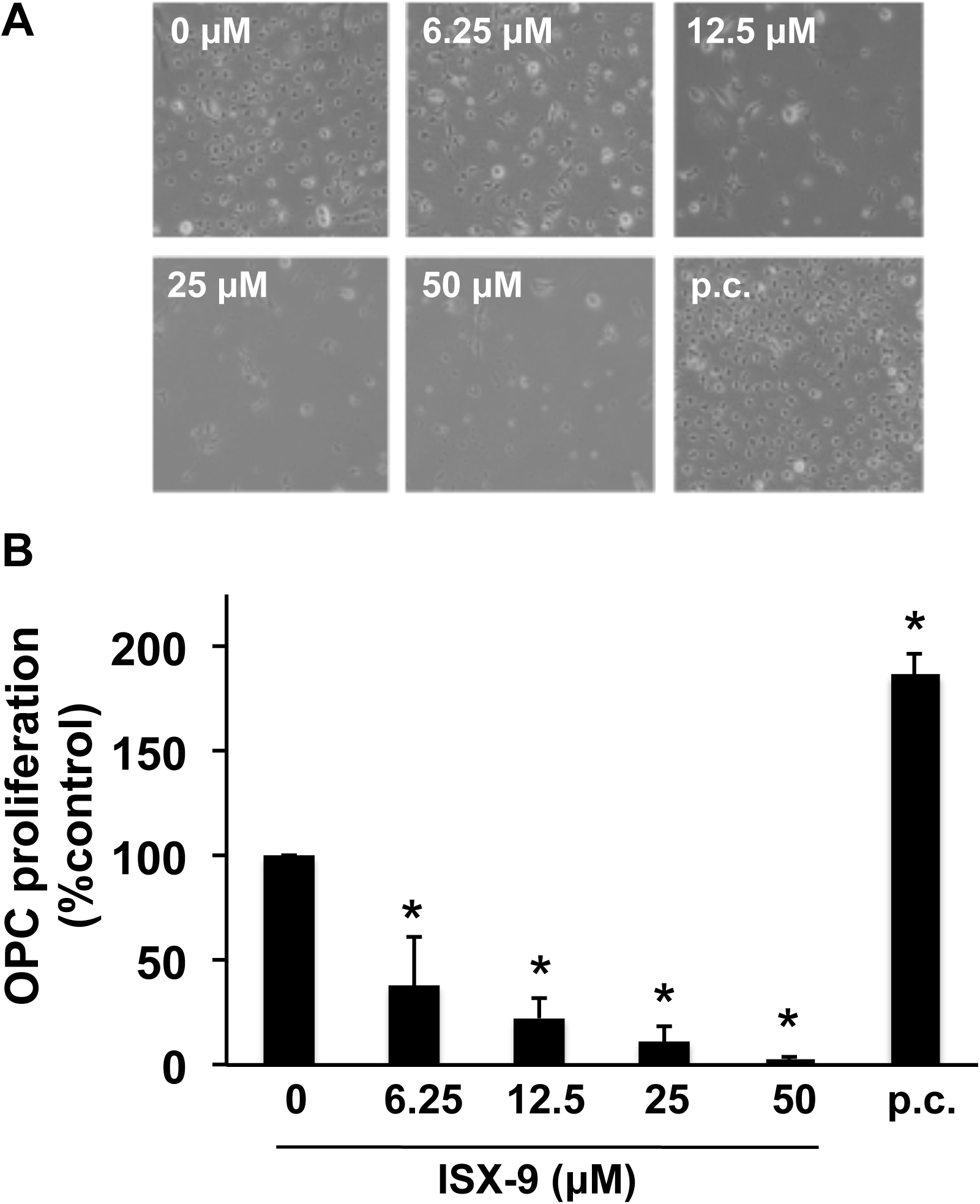
"In this study, we tested the effects of Isx-9 on the three major progenitor cell types in brain, and demonstrated that Isx-9 (i) promotes the differentiation from NSPCs into neurons, (ii) causes cell damage in OPCs, and (iii) decreases angiogenic tube formation in late-stage EPCs." [2]
It has been tested in the microgram to low milligram range (by those who have not done their research), and it has been noted to permanently improve memory, but at the cost of very strange side effects that last after dosing period (mood issues, perception changes, cold limbs).
Other notes:
- Continous ISX-9 treatment for 12 days on subgranular zone (SGZ) neuroblasts results in 50 and 86% increase relative to Vehicle SGZ Ki67+ cells but normalized after 30 days post injections. [4]
- ISX-9 had a brain tissue half-life of ∼25 min. [4][6]
- ISX-9 enhances the proliferation of neuroblasts and adult neurogenesis without exhausting the NSC pool. [4][5]
- ISX-9 is able to cross blood brain barrier. [5][6]
- ISX-9 is able to inhibit differentiation of neural progenitors into other cell types which makes it very target specific [1]
ISX-9 has problems, but serves as an example of how promoting neural stem/progenitor cells can be procognitive to a significant degree. If this can be done without negatively impacting other cell types, it could have a high potential for enhancing cognition.
Sources
Related
No related nodes found