If you have seen my post on PDE4D, you may understand the significance of microtuble-related proteins for high-level cognition. Proteins in the Golgi and pericentrosome contribute to microtuble nucleation, and microtubles are incredibly important as the underlying functional and structural factor for neurons.
CDK5Rap2 modulation may be a very interesting pathway for cognitive enhancement and improving models of neurodegeneration.
A little review on the last post: PDE4D interacts with PDE4D Interacting Protein (myomegalin), which is an important factor in microtuble (aka MT) nucleation and function. PDE4D also interacts with AKAP450 (AKA AKAP9) [1]. PDE4D is especially interesting due to its dlPFC-specifity [2], which is likely unique for the PDE4D-myomegalin pathway, however other microtuble-related proteins still have importance.
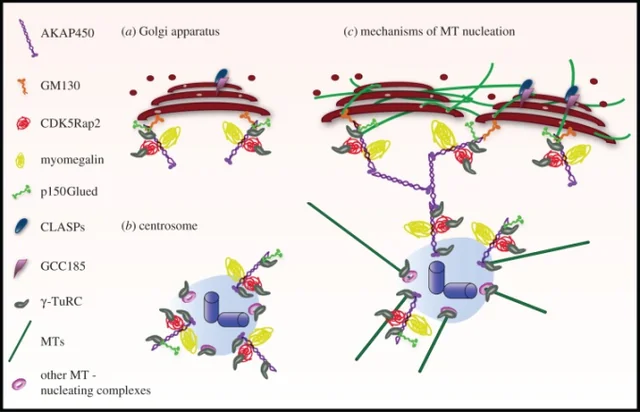
There are multiple other microtuble nucleating complexes other than the ones mentioned. One very important one, which I wanted to talk about today, is called CDK5Rap2 (AKA Cep215). CDK5Rap2 is a paralogue of myomegalin (PDE4DIP) that is necessary for the formation and stability of microtubles [3]. It is found both pericentrosomally and at the Golgi apperatus. It is a very important protein for the whole brain and body and it lacks much brain region specifity [4].
Not all microtuble-related proteins are located at the Golgi Apperatus (GA) - So far, five of the PCM proteins described (AKAP450, CDK5Rap2, myomegalin, CAP350 and pericentrin) have been found associated with the Golgi Apperatus in mammalian cells.
CDK5Rap2 deficiency is linked to microcephaly (MCPH), and is seen as the main underlying factor. This shows its importance as it directly controls brain development and size. Therefore, CDK5Rap2 potentiation could hypothetically increase brain size when combined with growth factors.
To back up this theory, An MRI study has demonstrated a link between common human variation in the CDK5RAP2 gene and brain structure. More specifically, associations were found between several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and brain cortical surface area and total brain volume.
CDK5Rap2 has been shown to bind to growing MT tips by associating with EB1, suggesting that it could, in this way, regulate the plus-end dynamics of MTs. CDK5Rap2 directly binds g-TuRC and works as a strong activator of MT nucleation through its g-TuNA motif.
CDK5Rap2 is difficult to modulate directly due to its lack of distinct binding sites and ligands. Then how can it be modulated? CDK5Rap2 binds to p25 (CDK5-p25), a form of CDK5R1 that serves as the activating subunit of CDK5, which is involved in the regulation of neuronal differentiation. Modulating p25 can effectively modulate CDK5Rap2 due to its direct interaction, and it also is quite selective.
Modulating CDK5 generally can have many offtargets due to its many interactions, so modulating p25 or other specific protein interactions/expressions rather than the whole of CDK5 unselectively is likely much superior.
In recent years increased cdk5/p25 expression has been demonstrated in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases [5]. The breakdown of cdk5/p35 into cdk5/p25 increases its kinase activity and neurotoxicity.
Tau pathology is heavily implicated in Alzheimer's, and is seen as the main resulting destructive pathway for the disease. Previously, Aβ (Beta Amyloid) was thought to be the main degenerative factor, however recent research has shown that tau is most likely a more important factor.
A CDK5 derived peptide CDK5-p25 inhibitor was developed by the Scripps Research Institute and is named CDK5i-FT [6]. CDK5i-FT is a 12-amino-acid-long peptide fragment derived from Cdk5 (Cdk5i) that is considerably smaller than existing peptide inhibitors of Cdk5 (P5 and CIP) but shows high binding affinity toward the Cdk5/p25 complex, disrupts the interaction of Cdk5 with p25, and lowers Cdk5/p25 kinase activity.
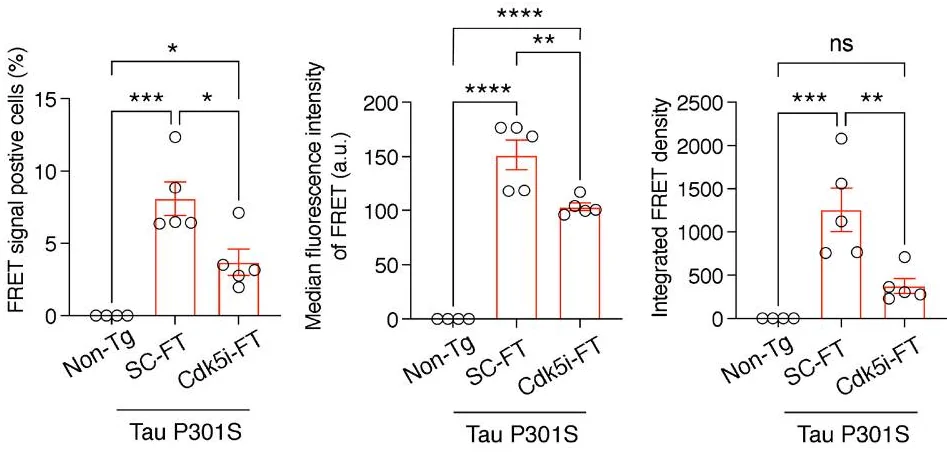
In the study referenced, CDK5i-FT ameliorated tauopathy and significantly reduced neurodegeneration in the models tested. The peptide was not tested in naiive models, so it is currently unknown how significant the effects are for healthy models, however it still is very interesting. Overexpression of Cdk5i peptide reduces Cdk5/p25 kinase activity but has no impact on the activity of Cdk5/p35 and Cdk1/Cyclin A complexes.
In 7 to 9-mo-old Tau P301S mice, 1 mo of CDK5i-FT treatment effectively rescues neuronal loss and memory deficits.
In recent years increased cdk5/p25 expression has been demonstrated in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. CDK5/p25 could phosphorylate other substrates such as tau and p53, as well as the retinoblastoma protein pRb. All these data lend credence to the hypothesis that cdk5/p25 acts as a master regulator of neuronal cell death. [5]
Combining different approaches of microtuble enhancement (nucleation/stability) with things like myomegalin enhancement and CDK5Rap2 enhancement likely is much superior than either one on their own. For a holistic cognitive enhancement, a multifaceted approach is likely the most effective method. What does this mean?
Simply put, CDK5Rap2, alongside PDE4DIP modulation could act as one of the most effective pathways for cognitive enhancement and neurodegeneration attenuation currently known.
The pathway of CDK5Rap2 and other interconnected microtuble-related proteins definitely warrant more investigation.
I encourage any readers who are interested in high-level neuroscience to look into the studies referenced, so that information here can be understood better.
Thanks for reading.