P7C3-A20
Pharmacology 
P7C3-A20 is a fluorinated enantiomer of P7C3, a neuroprotective aminopropyl carbazole agent discovered in 2010 [1]. It is a neurogenesis-inducing compound and neuroprotective.
It is thought P7C3-A20 (and P7C3) exert effects through activating the enzyme nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT). NAMPT is the rate-limiting enzyme in the NAD salvage pathway that converts nicotinamide to NMN, the precursor to NAD synthesis.
P7C3 also has seperate mechanisms, for example it is a PAM of GLP-1, a GSK-3 inhibitor, and a promoter of ADAM11 (related to mGluR3), however these pathways may be unique to P7C3 rather than P7C3-A20. [3]
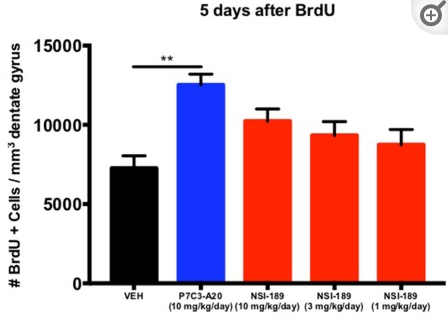
The proneurogenic efficacy of P7C3-A20 was compared to that of NSI-189, a proneurogenic drug currently in clinical trials for patients with major depression.
Orally-administered P7C3-A20 provided sustained plasma exposure, was well-tolerated, and elevated the survival of hippocampal BrdU+ cells in nonhuman primates without adverse central or peripheral tissue effects. [2]
In mice, NSI-189 was shown to be pro-proliferative, and P7C3-A20 elevated the net magnitude of hippocampal neurogenesis to a greater degree than NSI-189 through its distinct mechanism of promoting neuronal survival. Interestingly, P7C3-A20 seems to enhance hippocampal cell survival more than proliferation compared to NSI-189 [2]
After 38 weeks of daily oral exposure at 10 mg/kg dose of P7C3-A20 in nonhuman primates, tissues were comprehensively collected at necropsy and evaluated by a pathologist blind to experimental condition. No microscopic evidence of toxicology was detected in any of the tissues examined. [2]
Expected human dose is likely around the same dosage as NSI-189. Most effect ROA may be intranasal or oral. Something to note, is that at high concentrations of P7C3-A20 (>100nM), it induces spontaneous neurite degeneration [1] (which is not good), so it is advisible to keep a moderate dose. Saying this, the primate study saw no evidence of toxicity anywhere in the body associated with P7C3-A20 administration, so converting from that primate study to human dosage should be relatively safe.
It has a half-life in primates of about 4-8 hours.
Sources
Related
No related nodes found